Ubiquitin TUBE-Based Mass Spectrometry Proteomics
Advanced enrichment and analysis of polyubiquitylated proteins using our proprietary TUBE technology combined with state-of-the-art mass spectrometry
Need Help?

TUBE-Based Mass Spectrometry Proteomics
Traditional mass spectrometry–based proteomics approaches, such as SILAC (stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture), can be limited by low sensitivity and reproducibility, as well as high cost and long experimental timelines. LifeSensors’ Tandem Ubiquitin Binding Entities (TUBEs) bind polyubiquitin chains with high affinity (1–10 nM), addressing several of these limitations and enabling more robust enrichment of ubiquitylated proteins. LifeSensors has developed TUBEs selective for K63-, K48-, and M1 (linear) ubiquitin chains and is actively expanding this portfolio to include K6-, K11-, K27-, K29-, and K33-linked polyubiquitin chains.
When combined with targeted mass spectrometry, TUBE-based affinity enrichment provides a powerful platform for detecting changes in post-translational modifications and identifying disease-relevant signatures for both research and biomarker discovery. This ubiquitin proteomics technology enables the detection of ultra-low abundance ubiquitylated proteins from cells and tissues, supporting sensitive and biologically meaningful analysis of ubiquitin signaling pathways.
TUBE Enrichment Process
- Lyse cells
- Wash non-specific proteins
- Elute proteins
- Protease digestion
Resources Available
Download Sample Report PDF
TUBE Mass Spectrometry Proteomics Services
Proteomics of Induced Proximity-Based Degraders
TUBE enrichment allows for the most natural mechanistic validation of PROTACSs and Molecular Glues.
Tissue Analysis via TUBE-based Mass Spec
Using abundance measurements with ubiquitination data, mass spectrometry provides a systems-level view of how disease perturbs protein homeostasis.
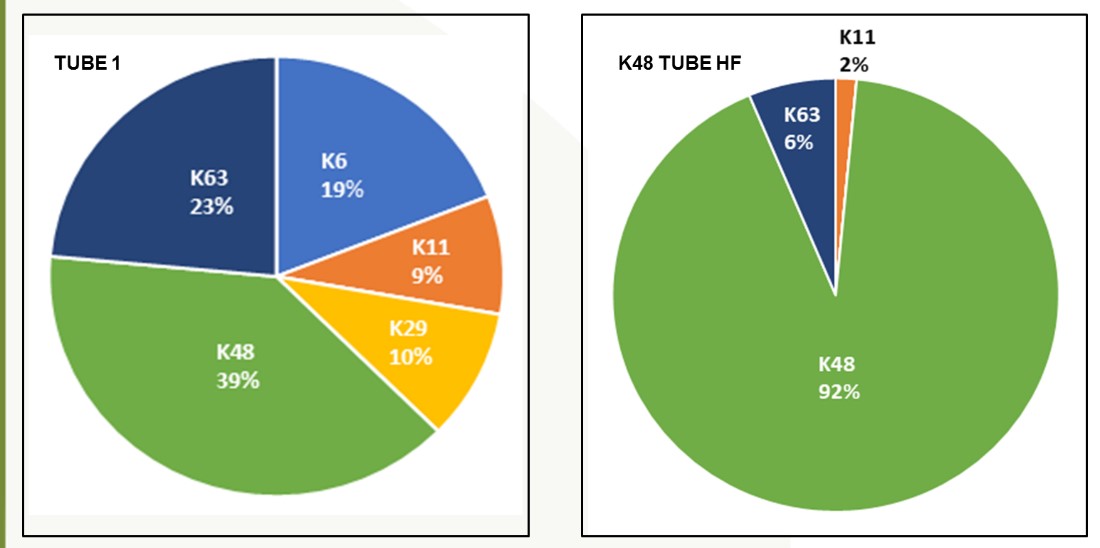
Chain Selectivity
Detailed analysis of the method of ubiquitination evaluates degradation (K48) vs trafficking (K63).
Substrate ID: DUBs & E3
Substrate identification for E3 ligases and Deubiquitinases to evaluate confounds and how they impact ubiquitination.
Whole Cell Proteomics
Evaluation of global proteome induced changes by PROTACs and small molecule drugs establishes efficacy and specificity of drug molecules.
Lysine Ubiquitination ID
Characterize ubiquitin chain types to evaluate degradation, localization or signaling.
- Core Benefits
Experimental Design Consultation
We are here to help you from the beginning, and are happy to sit down and help you design the best experiment to address your specific questions.
Competitive Pricing
We have competitively priced our analysis and offer custom services with the level of analysis that matches your needs and budget.
Fast & Professional Reports
We strive to deliver you accurate and professional reports quickly. From submission of samples, reports are typically delivered in 2-4 weeks depending on the complexity of project.
-
Proteomics of Induced Proximity-Based Degraders:
PROTACs/Molecular Glues/Ubiquitination Modifiers
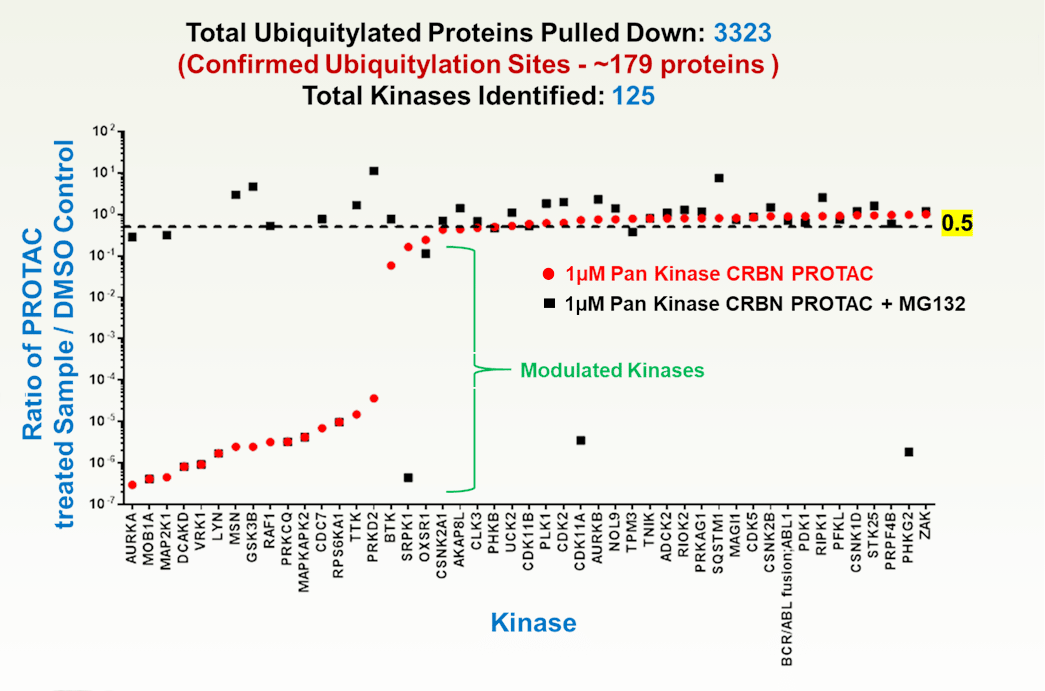
Mass spectrometry is a critical tool for evaluating PROTACs and molecular glues because it directly measures endogenous protein degradation and the ubiquitin-mediated mechanisms that drive targeted protein degradation (TPD). Proteomics can quantify changes in target protein abundance, confirm engagement of the ubiquitin–proteasome system through detection of ubiquitinated peptides, and distinguish true degradation from indirect effects. This direct readout is especially important for event-driven pharmacology, where transient compound binding leads to sustained protein loss.
Beyond confirming target knockdown, mass spectrometry provides a system-wide view of degrader selectivity and mechanism. Proteome-wide analyses can reveal off-target degradation, neo-substrates induced by molecular glues, and pathway-level consequences that are not predictable from binding or reporter assays. Time-resolved MS experiments further help dissect the sequence of ubiquitination and protein clearance, supporting rational optimization of degrader potency and specificity.
Luciferase-based assays remain valuable for early screening due to their speed and sensitivity, but they rely on engineered reporter systems that may not reflect endogenous regulation. Changes in reporter signal can arise from transcriptional effects, cytotoxicity, or reporter instability rather than true protein degradation. In contrast, mass spectrometry provides unambiguous, physiologically relevant evidence of target degradation and selectivity, making it the gold standard for mechanistic validation of PROTACs and molecular glues. TUBE based pulldown, evaluation and reporting allows LifeSensors to offer a top of the line service to evaluate the impact of PROTACs and Molecular Glues.
- Tissue Analysis via TUBE Mass Spectrometry Proteomics
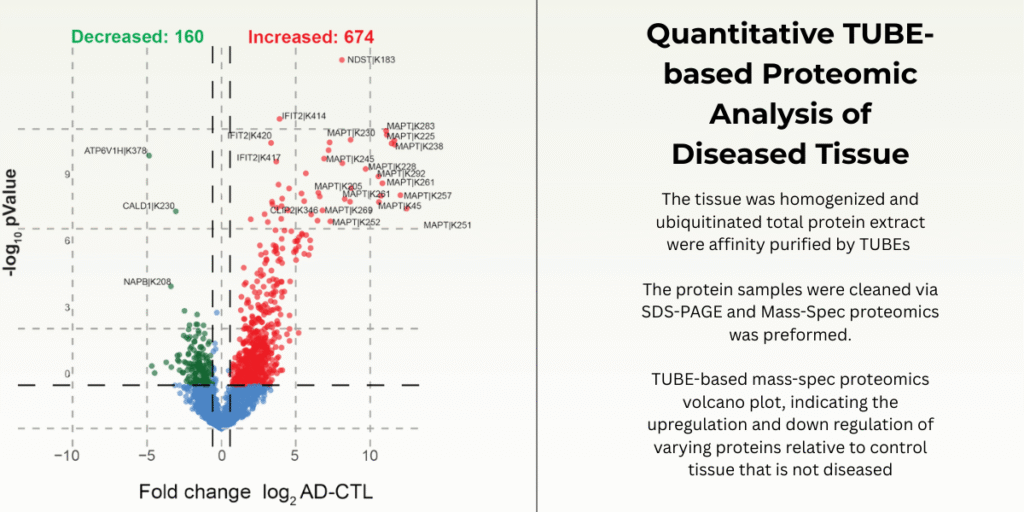
Mass spectrometry–based proteomics is especially important for studying disease because it allows direct measurement of protein abundance changes while also capturing regulatory mechanisms that cannot be inferred from gene or mRNA data alone. In many diseases, proteins are up- or down-regulated not because of altered transcription, but because of changes in stability and turnover. Since proteins are the functional molecules that execute cellular processes, observing their actual levels provides a more accurate picture of disease biology than genomics or transcriptomics alone.
Ubiquitination plays a central role in controlling protein degradation, signaling, and cellular quality control, and its dysregulation is a hallmark of many diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Mass spectrometry proteomics enables the identification and quantification of ubiquitinated proteins and specific ubiquitination sites, allowing researchers to see which proteins are being selectively targeted for degradation or altered signaling. This is critical for understanding disease mechanisms where abnormal protein accumulation or excessive protein loss drives pathology, such as the buildup of misfolded proteins in neurodegeneration or the enhanced degradation of tumor suppressors in cancer.
By integrating protein abundance measurements with ubiquitination data, mass spectrometry provides a systems-level view of how disease perturbs protein homeostasis. Researchers can distinguish whether changes in protein levels arise from altered synthesis or from ubiquitin-mediated degradation, and they can map entire pathways affected by disrupted ubiquitin signaling. This makes mass spec proteomics a powerful tool for identifying disease biomarkers, uncovering therapeutic targets within the ubiquitin–proteasome system, and evaluating how drugs modulate protein stability and turnover in disease contexts.
LifeSensors’s TUBEs offers the most natural way of studying ubiquitination without modifying the target, or the ubiquitin chain, especially important for avoiding artifacts in such a valuable research tool.
- Experimental Data
In-house Data
Below are examples of data generated using TUBE-based mass spec technology with pan-selective TUBEs. Here, the ubiquitinated proteins have been differentiated from whole cell lysate. This methodology is sensitive enough to detect the number of ubiquitin sites on a given protein.
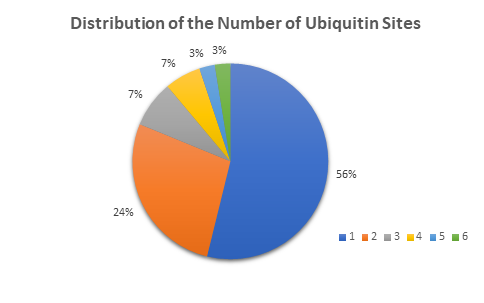
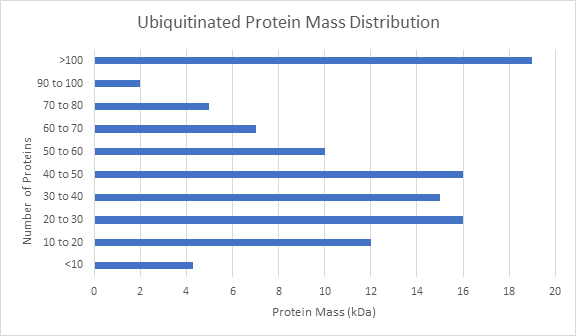
When studying the effects of a drug or genetic knockout, global shifts in the ubiquitome is a good place to start your analysis. Other global analysis provided by LifeSensors includes protein mass distribution of all proteins as well as ubiquitinated proteins.
- Published Data
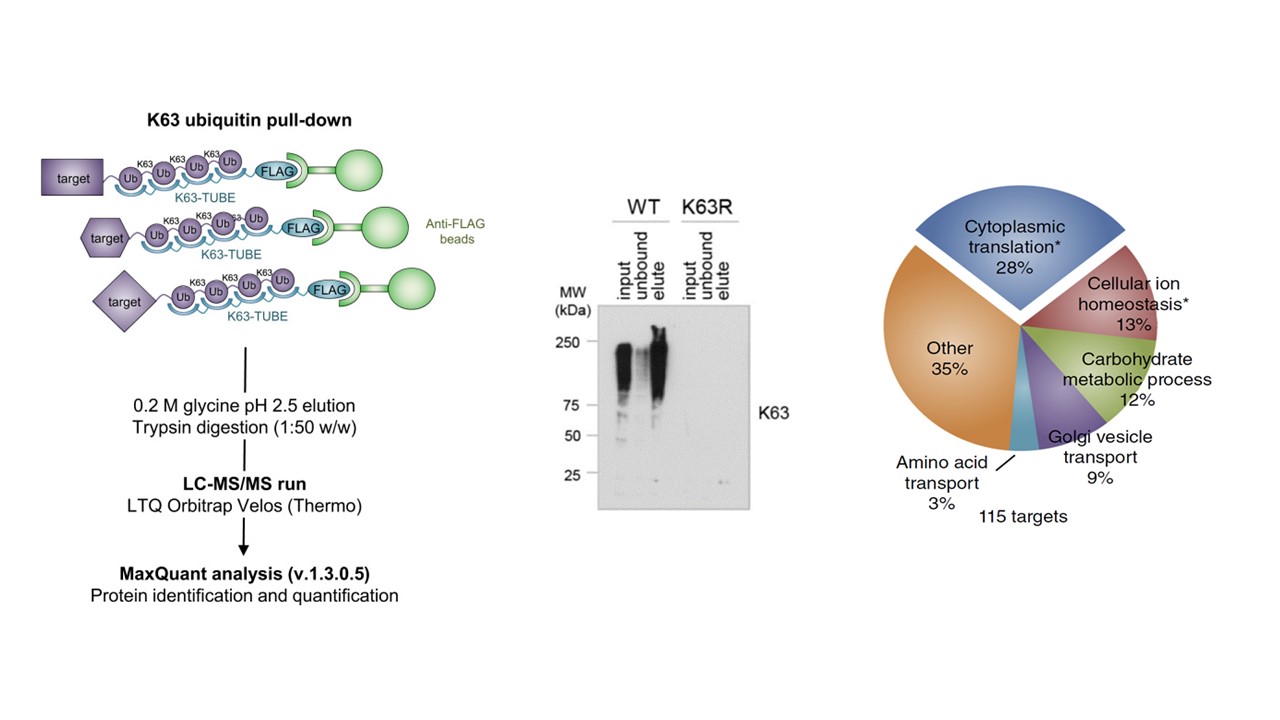
- Silva et al. Study
- Mata-Cantero et al. 2016
In 2016, Mata-Cantero et al. used TUBE-based mass spectrometry to identify major components of the ubiquitin proteome of both Plasmodium falciparum and its host during different life stages.
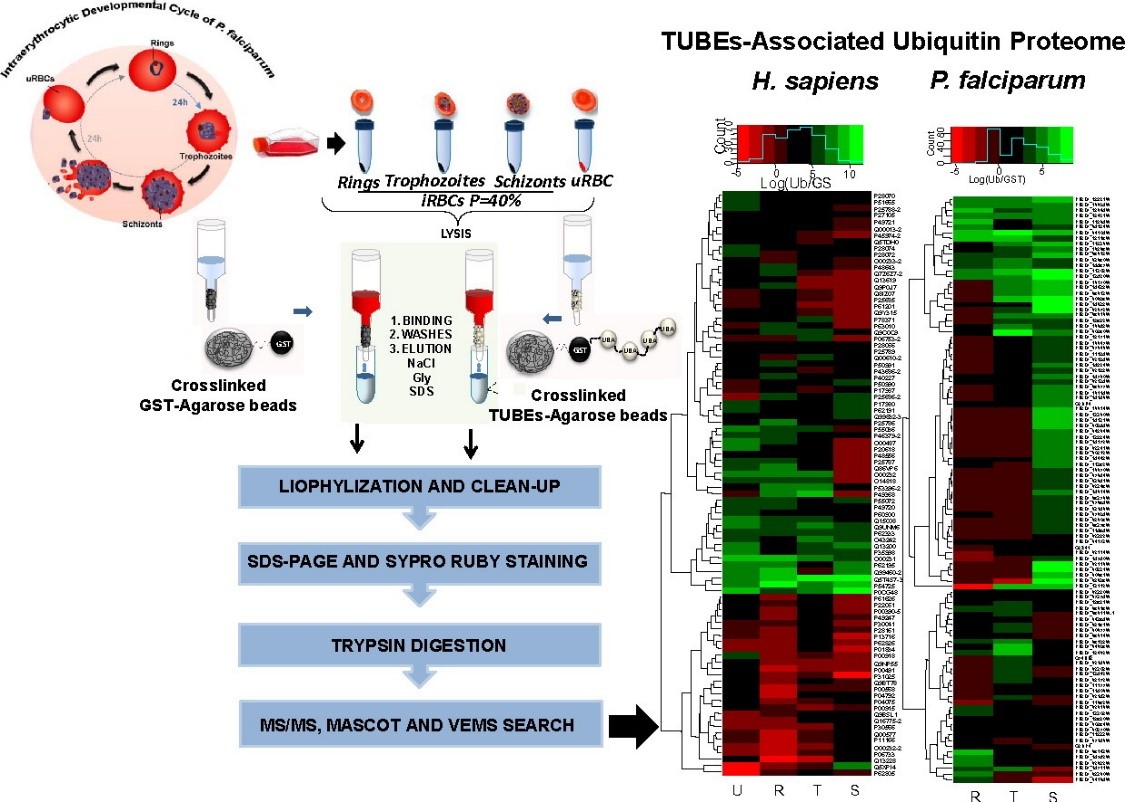
Intraerythrocytic Developmental Cycle of P. falciparum is shown. Synchronized P. falciparum iRBC at 40% parasitaemia from rings, trophozoites and schizonts stages were collected and frozen. TUBE enriched proteins from iRBC at different stages and uRBC were captured using TUBEs or GST (control) previously crosslinked with DMP to agarose beads. After exhaustive washes, proteins captured were eluted, cleaned by precipitation and resolved by electrophoresis (PAGE). Bands with proteins were analyzed by LC-MS/MS.
- Substrate ID: DUBs and E3s
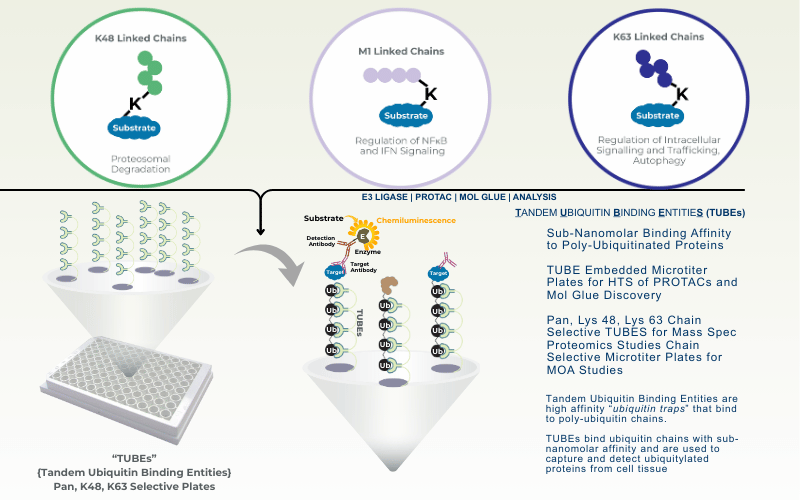
The Ubiquitin Proteasome System (UPS) controls the principal functions of almost all the cellular proteins of human cells and failures in this system often contribute directly or indirectly to the pathogenesis of many diseases, including cancer, inflammation, and neurodegeneration. There are ~100 Deubiquitinases (DUBs) encoded in human genome and the functions of most of these DUBs remain unknown. Identification of substrates of individual DUBs is an essential step to unravel cellular functions of DUBs.
Not only limited to DUBs, there are ~700 E3 ubiquitin ligases encoded in human genome and the functions of most of these E3s remain unknown. Recent development of PROTAC drugs to recruit E3 ligases and degrade therapeutic proteins highlight the value of studying E3 ligases. Substrate identification in individual E3 ligases is an essential step to unraveling cellular functions of E3s and identifying novel therapeutic targets. LifeSensors can help you identify the substrates of your preferred E3s and DUBs.
- Advantages of Choosing LifeSensors For Your Drug Discovery Project
In Vitro & In Cell Assays
Comprehensive assays to identify DUB & E3 substrates in controlled environments and cellular contexts
Human Protein Array
Advanced TUBE technology enables identification of direct deubiquitination targets
Substrate Trapping & Proteomics
State-of-the-art proteomic analysis to identify endogenous substrates with precision
Orthogonal Validation
Rigorous validation of substrates through independent orthogonal assay methods
- Whole Cell Proteomics
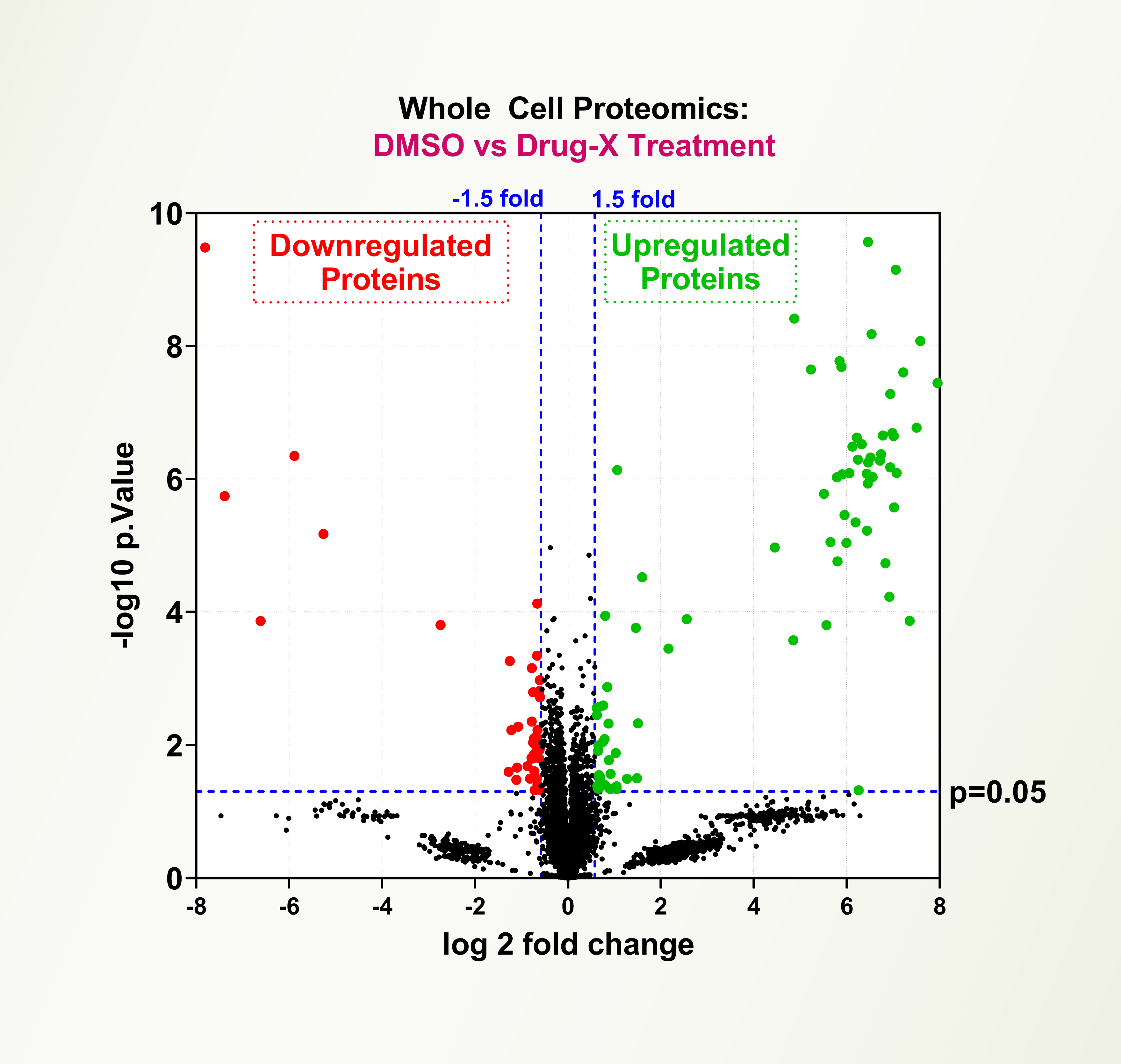
The Ubiquitin Proteasome System (UPS) controls the principal functions of almost all the cellular proteins of human cells, and failures in this system often contribute directly or indirectly to the pathogenesis of many diseases, including cancer, inflammation, and neurodegeneration. There are ~700 E3 ubiquitin ligases and ~100 deubiquitinases encoded in the human genome and the functions of most of these E3s and DUBs remain unknown. Recent development of PROTAC drugs to recruit E3 ligases and degrade therapeutic proteins highlight the value of studying E3 ligases. Evaluation of global proteome changes by PROTACs and small molecule drugs is an important tool to establish efficacy and specificity of drug molecules. LifeSensors offers whole cell proteomic services to characterize small molecules and PROTACs.
Service Highlights
- Robust proteomic profiling platform
- Effect of PROTACs, molecular glues and small molecule ligands on global proteome
- Target specificity and Tissue specificity of drugs
- Enables novel target and pathway discoveries
- Ubiquitin Chain Diversity ID Target / Lysine Ubiquitination ID
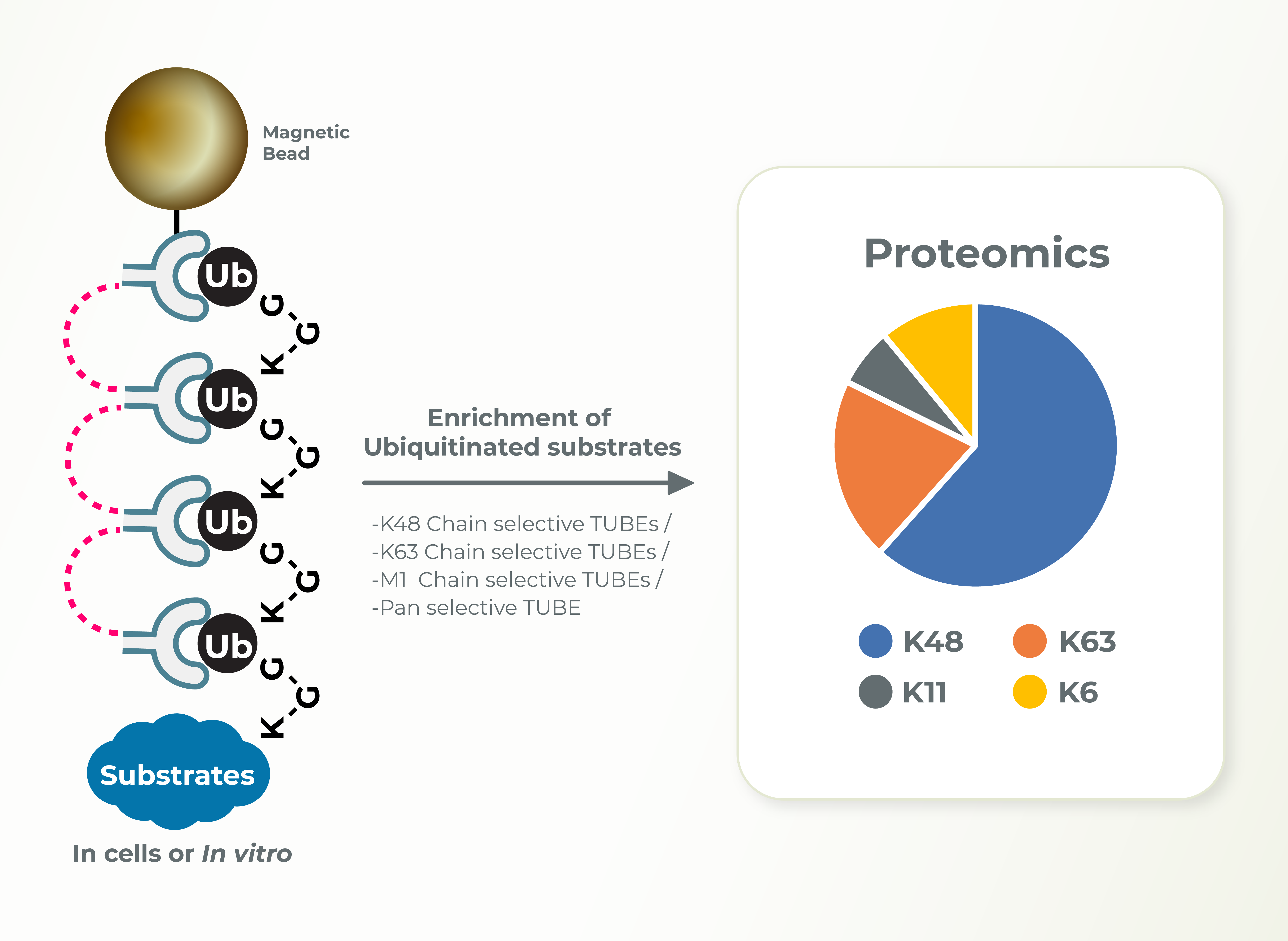
The Ubiquitin Proteasome System (UPS) controls the principal functions of almost all the cellular proteins of human cells and failures in this system often contribute directly or indirectly to the pathogenesis of many diseases, including cancer, inflammation, and neurodegeneration. There are ~700 E3 ubiquitin ligases encoded in human genome and the functions of most of these E3s remain unknown. E3 ligases build diverse ubiquitin chain linkages on substrates that can determine the fate of the substrate. Whereas K48-linked ubiquitin chains promote proteasomal degradation of substrates, K63-linked ubiquitin chains are associated with signaling and localization. Identification of the type of ubiquitin linkage can provide insights into the cellular functions of E3s and substrates. LifeSensors can perform these studies using linkage specific TUBEs very efficiently and in a timely manner for the clients.
Service Highlights
- Cell-based assays to identify endogenous substrate ubiquitination
- Identify the diversity of ubiquitin chain linkages
- Study the effect of PROTACs or small molecules chain diversity
- Mass Spec Proteomics Key Products