LifeSensors discovered that human SUMO is superior for E.coli expression of some of the proteins in E.coli. Therefore we developed human SUMO system and called it SUMOpro3. SUMOpro3 tag is best cleaved with SUMO protease 2, that is a human de-SUMOylase. Please contact us to help you evaluate the best system for your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Find answers to common questions about our biotech products, protocols, and services. Our comprehensive FAQ covers everything from PROTACs to mass spectrometry.
Need Help?
This is the heading
Our scientific support team is here to assist you.
- General Questions
How do I submit an inquiry or service request?
You can submit an inquiry using the Contact Us form under the About Us tab. Please provide your contact information and details about your project.
When submitting your request, include:
- Target protein(s) you wish to study
- Quantity of compounds to be tested
- Type of assay (if known)
- Any other relevant project details
Alternatively, you may contact us directly:
- Product & technical inquiries: customerservice@lifesensors.com
CRO services, custom products, or service requests: bd@lifesensors.com
Does LifeSensors have international distributors?
Yes. LifeSensors works with multiple international distributor partners.
International (non-US) customers should contact their local distributor for product orders.
A full list of distributors is available on the Distributor Page.
Where can I access details on the protocol for the reagent or assay kit I ordered?
Yes. LifeSensors works with multiple international distributor partners.
International (non-US) customers should contact their local distributor for product orders.
A full list of distributors is available on the Distributor Page.
Where can I find product datasheets?
Protocols for reagents and assay kits are available on each product page under the Documents section.
For additional technical support, please contact customerservice@lifesensors.com.
How do I freeze-thaw TUBEs and recombinant proteins?
How do I convert mg/mL mass concentration to molar concentration?
To convert mg/mL to molar concentration, you need the molecular weight of the protein.
Example:
Wild-type ubiquitin has a molecular weight of 8.56 kDa.
A 5.0 mg/mL solution is calculated as:
5.0 ÷ 8.56 = 0.584 mM (584.0 µM)
What are the storage conditions for recombinant proteins?
Recombinant proteins should be stored at −80°C.
How do I send samples for screening?
We accept compounds in the following formats:
- Powder form
- DMSO stocks
- Aqueous solutions
Samples may be shipped as:
- Individual vials
- 96-well plates
- 384-well plates
Sample shipment address:
LifeSensors, Inc.
ATTN: Karteek Kadimisetty
271 Great Valley Parkway
Malvern, PA 19355
Can I get a custom protein tag or custom labeling for my E3 or DUB of interest?
Yes. We offer E3 or DUB proteins with custom tags or labeling.
For custom product or service requests, please contact:
bd@lifesensorsstg.com
How do I approach using SUMO-tag for commercial applications with a license?
For licensing inquiries related to SUMO-tag usage, please contact:
bd@lifesensors.com
- PROTACs
What is a PROTAC?
PROTAC stands for Proteolytic Targeting Chimera that has multiple functional units that engage specific proteins of interest within the cells so that can be degraded using cell’s own ubiquitin proteasome system. One of the ligand pf the PROTAC typically refers to “warhead” targets protein of interest and another ligand often refers to “anchor” is used to recruit E3 ubiquitin ligase. Both the warhead and anchor are connected by a chemical linker making a PROTAC.
Does linker length and linker type are crucial for effective PROTAC design?
What are different types of assays LifeSensors offers for PROTAC Drug Discovery?
LifeSensors offer a suite of assays that characterizes a PROTAC from its affinity to bind with proteins of interest to cellular assays that can demonstrate degradation and selectivity.
1. Biophysical assays to monitor ternary complex formation and validating ligand affinity
2. In vitro ubiquitination assays to validate a functional ternary complex
3. Cell based ubiquitination assays to validate cell permeability and function in cells
4. Degradation assays to validate degradation and demonstrate DC50 & selectivity
5. Mass spectrometry to demonstrate selectivity
What type of polyubiquitination can be detected with LifeSensors' PROTAC Assay Plate?
Since our plates use pan-selective TUBEs, any type of polyubiquitination with any of seven lysine residues (K6, K11, K27, K29, K33, K48, K63) will be detected.
Does LifeSensors' PROTAC Assay Plate work for Molecular Glue discovery?
Yes, our PROTAC Assay Plates, along with our In vitro ubiquitination assay kit, have been designed to work with both PROTACs and Molecular Glues.
What is the principle of LifeSensors' PA950 PROTAC Assay Plate?
The PROTAC® Assay Plate is a sandwich-based assay in which polyubiquitinated proteins from cell lysates are captured in the wells of a precoated microtiter plate using a proprietary polyubiquitin binding reagent. Proteins that are not polyubiquitinated/unbound are removed by washing and then an antibody directed against the target protein is added followed by washing. Lastly, a secondary antibody conjugated to horse radish peroxidase (HRP) is used to measure the bound target antibody with detection reagents and a luminescence microplate reader.
What is the principle of LifeSensors' PA770 In Vitro Ubiquitination Assay Kit?
The In vitro ubiquitination kit has been developed to establish a high throughput approach that can accurately predict PROTAC efficiency by monitoring the protein’s intrinsic ability to get ubiquitinated. We offer this kit for three E3 ubiquitin ligases: Cereblon, VHL, and HDM2 to monitor PROTAC mediated ubiquitination for target of choice. At the core of the assay, microtiter plate strips, pre-coated with a proprietary TUBE reagent (assay plate) are used for the capture of polyubiquitin chains formed in a PROTAC dependent reaction.
The signal generated by captured polyubiquitylated product in this “sandwich” ELISA-like assay is a quantitative measure of PROTAC activity. Furthermore, this detection strategy does not require additional non-native tagging or labeling of ubiquitin, which could lead to experimental artifacts.
What is the difference between LifeSensors' PA950 kit and PA770 kit?
The PA950 kit was created to be used as a cell-based ELISA while the PA770 kit is an Invitro Based ELISA.
What is the PA950 Decomplexing Buffer?
For some targets, the decomplexing agent enhances the signal to background. We recommend the use of the decomplexing agent prior to analysis with PA950. The use of the decomplexing agent disrupts any native protein complexes that might be part of ubiquitin complexes. Using this urea based decomplexing agent results in reduced background signal, resulting in a better signal-to-background ratio. This buffer is available for purchase on the LifeSensors website here.
Do you offer PROTAC design and Medicinal Chemistry?
Does LifeSensors offer services to screen ligands for novel E3 ligases for PROTAC applications?
- TUBEs
What are the different types of pan-TUBEs LifeSensors sells?
LifeSensors’ TUBE (Tandem Ubiquitin Binding Entity) technologies are industry-leading tools to detect and enrich/purify poly-ubiquitylated proteins from cell lines, tissues, and organs. LifeSensors has two commercially available pan-TUBEs (TUBE1 and TUBE2). Both TUBE1 and TUBE2 come in various flavors such that they can be used for far-Western detection (FLAG, Biotin), enrichment/purification (linked to Agarose and Magnetic beads), and in vivo imaging (TAMRA, FITC-attached) applications. For more information, please see our TUBEs page.
What is the difference between TUBE1 and TUBE2?
Does LifeSensors sell linkage-selective TUBEs?
What is the difference between K48 TUBE and K48 TUBE HF?
Which TUBE is more efficient at capturing human proteins as opposed to rodents, plants or yeasts?
Have TUBEs been tested for plants and other organisms?
How much protein (cell/tissue extracts) do I need to add to TUBEs?
How do I elute poly-ubiquitylated proteins from TUBEs?
How do I elute poly-ubiquitylated proteins for mass spectrometric analysis?
What are the controls for TUBEs function?
Positive control: How do I know that TUBEs work?
The properties of TUBEs have been well characterized and published. Each TUBE lot is quality controlled for overall binding capacity and the pull-down efficiency of polyubiquitylated proteins using cell lysate.
Negative control: How do I know that TUBEs aren’t yielding an artifact?
We recommend to include a negative control in your pull-downs that contains the quenched agarose resin (LifeSensors cat # UM400).
Can I enrich mono-ubiquitylated proteins with TUBEs?
Does LifeSensors have a TUBE product to detect SUMOylated proteins?
What are the assays developed by LifeSensors using TUBE technology?
What is UbiTest?
The UbiTest platform replaces traditional immunoblotting methods for measuring cellular ubiquitylation, enabling simple comparisons of substrate ubiquitylation levels between samples and determination of ubiquitin chain linkage types. UbiTest is based on TUBE technology for enriching polyubiquitylated proteins. By visualizing the ubiquitylated fraction both with and without DUB digestion of polyubiquitin chains, UbiTest streamlines the confirmation of ubiquitylation status. For more information about UbiTest, please also visit our UbiTest product pages, where you can purchase off-the-shelf assay kits for performing UbiTest in your own lab.
LifeSensors has also developed High-Throughput (HT) UbiTest which is a customized medium-throughput assay for absolute quantification of ubiquitylated substrate levels in cells that combines UbiTest principles and TR-FRET technology. Please contact us if you like to develop similar assays for your target protein.
What is UbiQuant S?
Does LifeSensors offer services to develop a customized assay for a target protein?
Does LifeSensors offer TUBE-based proteomics services?
What are the storage conditions for Magnetic Beads?
Magnetic beads should be stored at 4°C after arrival. After use any unused beads should be stored with PBS + 20% EtOH.
What are the storage conditions for Agarose Beads?
Agarose beads should be stored at 4°C after arrival. Do not freeze the agarose beads.
Are there loading controls for Western blots after TUBE enrichment?
Unlike with whole cell lysate, probing for a housekeeping protein, like GAPDH, is not possible after TUBE enrichment. Thus, we recommend completing pulldowns from all experimental conditions using the same quantity of lysate and the same amount of TUBE.
When should I use a solution-based pulldown vs. a matrix-based pulldown?
What are the differences between Agarose TUBEs and Magnetic TUBEs?
Magnetic TUBEs offer various advantages over agarose TUBEs. Agarose TUBEs require centrifugation steps for separation of beads from the solution phase. Magnetic beads offer an advantage in terms of ease of separation, as well as their ability to be used in bead-based ELISAs.
What is the difference between Magnetic TUBE1 and High-Capacity Magnetic TUBE1?
High-Capacity TUBE1 (UM501M) were designed by coating polymeric high-capacity magnetic beads to allow superior enrichment of polyubiquitinated proteins along with minimizing non-specific binding to proteins in tissue and cellular lysates. Magnetic TUBE1 beads (UM401M) are 1 µm and High-Capacity TUBE1 beads (UM501M) are 2.8 µm in diameter.
How do I perform a TUBE pulldown?
Depending on the type of TUBE purchased, the protocol differs slightly. Please refer to the manual for each specific product when performing a pulldown. This manual can be found on the product page for each specific TUBE.
For Western blotting, what antibodies should I use?
How do I reduce background and non-specific binding in TUBE pulldowns?
Can I use TUBEs as detection reagents?
- SUMO
What is the advantage of using the SUMO system?
What proteins have been previously expressed with SUMO?
What is the difference between SUMOpro and SUMOstar?
What host models are available?
We offer systems that are optimized for:
– Bacterial: E.coli
– Yeast: S.cereviseaand P.pichia
– Baculoviral/Insect cell system
– Mammalian: HEK293and CHO cells
What is the SUMOpro3 system?
LifeSensors discovered that human SUMO is superior for E.coli expression of some of the proteins in E.coli. Therefore we developed human SUMO system and called it SUMOpro3. SUMOpro3 tag is best cleaved with SUMO protease 2, that is a human de-SUMOylase. Please contact us to help you evaluate the best system for your specific needs.
What is included in a kit?
What is the best way to ensure the protease removed the SUMO tag?
What is the SUMO tag system?
How do I approach using SUMO-tag for commercial applications with a license?
Please contact bd@lifesensors.com for licensing inquiries.
- Kits & Plates
What lysis buffer should I use for cell lysis?
Can I use LifeSensors' plates only for PROTACs?
What E3 ligases are offered for PA770 In vitro ubiquitination assay kit?
What secondary antibodies are offered for PA770 In vitro ubiquitination assay kit, and how do I know which one to use?
- DUBs and Ligases
What is a DUBTAC?
DUBTACs, or DeUBiquitinating TArgeting Chimeras, recruit DUBs to a target protein and remove ubiquitin chains, resulting in stabilization of target proteins.
DUBTACs consist of three components:
DUB recruiter
Target protein binder
Linker connecting both entities
DUBTACs restore protein levels, function, and rescue target proteins from degradation via the proteasome.
Do you offer custom assay development for DUBs and E3 ligases?
What is the ideal substrate for measuring DUB activity?
How do I choose a DUB panel for testing selectivity of my compounds?
How do you measure E3 ligase activity?
How do I choose an E3 ligase panel for testing selectivity of my compounds?
How do you prefer to receive compounds for testing?
Do you sell inhibitors or agonists to use as an internal control in biochemical assays?
Why doesn't my assay work?
- Ubiquitin & Ubiquitin Chains
What assay buffer do I use for testing my chains with DUBs?
What temperature should I store my chains at?
Why do I see multiple bands on my gel/Western Blot while cleaving?
Depending on the activity of the DUB and which DUBs you are using, you can get complete or partial cleavage. Always include a “-DUB” control to see what the chain looks like before cleavage. If you cleave a tetra-ubiquitin, for example, then you should end up with a gel that has a band at Tetra-, Tri-, Di-, and monoubiquitin. This means the DUB successfully cleaved the ubiquitin. If you see only monoubiquitin and you started with a tetra-ubiquitin, then you had 100% cleavage.
If you are just running a Western blot, we do not recommend loading more than 50 ng at a time as overloading could yield “smudged” Western Blot results.
What temperature should I incubate my ubiquitin chain cleavage reactions?
Will my chains get damaged after multiple freeze thaws?
If I purchase the "Non-Cleavable" Ubiquitin and a "DUB-Resistant" Ubiquitin, what should I expect, and what is the difference between the two?
What is the difference between Di, Tri, and Tetra chains and the others?
What are K to R Ubiquitin Mutants listed on your website?
Why are mutations/linkages at lysines?
What is the purpose of products like UbRh110, UbAMC, K48-UbRh110 etc.?
Ubiquitin Rhodamine and AMC are ubiquitin derivatives used as substrates to test the activity of DUBs. When the DUB cleaves Ubiquitin from Ub-Rhodamine or UbAMC, the release of free Rhodamine and AMC results in an increase in fluorescence. These substrates allow for simple, fast, quantitative, and real-time monitoring of DUB activity.
K48 Tetra Ub linked Rhodamine is the same as above but meant for testing DUBs that are specific to K48 chains.
- Mass-Spectrometry
What are the advantages of TUBE-based mass spec?
What are the disadvantages of traditional methods?
What can I expect to get out of a mass spec service?
Clients receive their processed data in an excel file, as well as a summary report. We include graphical representations of ubiquitylation tends of your proteins. You will receive professional support when analyzing your data. See example report.
- Written report with summary of the TUBE based mass spec proteomics data, with sample prep protocols and LC-MS methods implemented for given samples along with sample description.
- Total Ubiquitinated identified will be presented in a list, as well as being organized on a distribution chart to show proportions.
- Total peptides identified will be presented in a list with length and mass information.
- Additional bioinformatic analysis for getting functional perspective of Proteomics data like DE analysis, cluster analysis and pathway & network analysis are available upon request at addition costs.
What is the typical work flow?
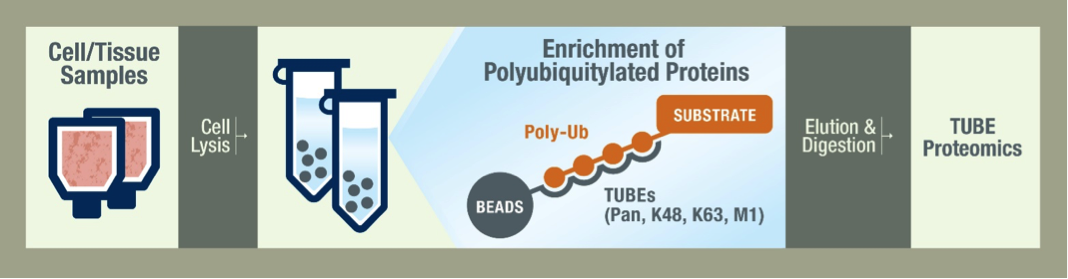
What is the required amount of starting material?
Do you recommend duplicates? Triplicates? ?
What is the turnaround time?
What type of control samples do you recommend?
Is this analysis quantitative?
- Thermal Shift & SPR
What is thermal shift assay (TSA)?
What is the principle of thermal shift assay?
How much protein is needed in a thermal shift assay?
What equipment is needed for running a thermal shift assay?
Do thermal shift assays work on all proteins?
What solvent is used for thermal shift dye?
What is SPR Assay?
Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) is an optical technique for detecting the interaction of two different molecules. One molecule (the ligand) is immobilized on a gold-coated surface, while another molecule (the analyte) is injected over the surface. The technique measures a change in refractive index at the surface, which is directly proportional to the change in mass. Both protein-protein and protein/small molecule interactions can be investigated with this method. Binding response units (RUs) are measured in real-time and analyzed to determine kinetic parameters including the binding affinity (KD).
