By: Derrick Padykula
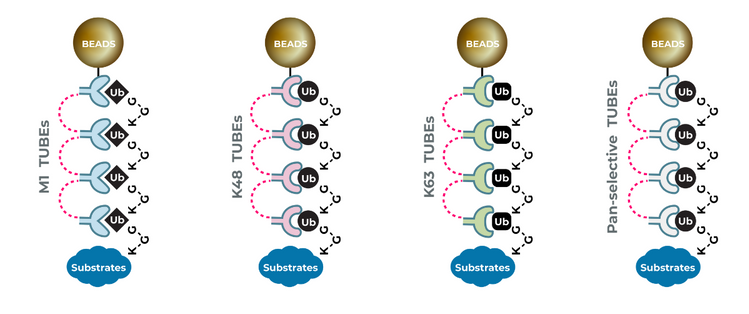
Ubiquitination, a ubiquitous cellular process, involves attaching ubiquitin to target proteins, influencing crucial cellular functions such as degradation, cell signaling, apoptosis, protein processing, immune response, and DNA repair. The specific ubiquitin chain type, whether M1, K6, K11, K27, K29, K33, K48, or K63-linked, dictates the downstream processing of the target protein. Delving into ubiquitination is paramount for understanding cellular processes, and LifeSensors’ groundbreaking technology, TUBEs (Tandem Ubiquitin-Binding Entities), takes this exploration to new heights. TUBEs harness the strength of multiple Ubiquitin Binding Domains (UBDs) to exhibit high nanomolar binding affinities (Kds) to ubiquitin chains, circumventing the need for labor-intensive methods like immunoprecipitation or ubiquitin antibodies.
Unleashing TUBEs’ Potential
LifeSensors offers both chain-selective and pan-selective TUBEs, providing researchers with unparalleled versatility. TUBE1 and TUBE2, pan-selective TUBEs, bind to all ubiquitin chain linkages, enabling the comprehensive study of ubiquitinated proteins or the entire ubiquitome.
Fine-Tuning with Selective TUBEs
For those seeking specificity, LifeSensors presents specialized TUBEs tailored to distinct ubiquitin linkages:
- K48-Selective HF TUBE: Demonstrating enhanced selectivity for K48-linked polyubiquitin chains, this variant serves as a powerful tool for studying protein degradation, a crucial aspect of the cell’s quality control mechanism.
- K63-Selective TUBE: Boasting a 1,000 to 10,000-fold preference for K63-linked polyubiquitin chains, this TUBE is an invaluable resource for investigating autophagy–lysosome-mediated proteolysis, DNA repair, and various signaling pathways.
Applications of TUBEs
TUBEs serve as versatile tools with a broad range of applications. They are utilized in various detection methods, acting as reagents for western blotting, fluorescence, and for measuring binding affinity or specificity through techniques like surface plasmon resonance (SPR), calorimetry, or thermophoresis. TUBEs also play a crucial role in identification methods, facilitating the affinity purification (pull-down) of ubiquitylated proteins, which can be detected using target-specific antibodies in western blotting or mass spectrometry. Additionally, TUBEs find application in quantifying total or individual ubiquitylated proteins and characterizing associated functions, employing formats like protein arrays or High Throughput Screening (HTS) techniques such as TUBE-AlphaLISA and TUBE-DELFIA. Furthermore, they contribute to identifying specific deubiquitylases (DUBs) for a given substrate, as demonstrated by the UbiTest assay.
In the pursuit of unraveling the intricacies of cellular processes, LifeSensors’ Chain-Selective and Pan-Selective TUBEs stand as trailblazers, providing researchers with unprecedented precision in dissecting ubiquitin signaling pathways and studying Targeted Protein Degradation (TPD). With a wide variety of applications, including mass spectrometry, high throughput screening, fluorescent microscopy, and more, these innovative technologies not only amplify our understanding of diverse ubiquitin chain linkages, but also lay the foundation for groundbreaking discoveries in cellular biology, disease mechanisms, and TPD. Whether it’s the targeted insights offered by Chain-Selective TUBEs, or the panoramic view provided by Pan-Selective TUBEs, LifeSensors empowers researchers to navigate the complex language of ubiquitin signaling. As we journey into the future, these TUBEs promise not only new insights into cellular functions but also hold the key to unlocking the ability to study therapeutic interventions for a myriad of conditions.
The Phospho-TUBE Advantage
In the relentless pursuit of precision in ubiquitin research, LifeSensors is working to develop a Phospho-TUBE, a cutting-edge technology poised to revolutionize the study of phosphorylated ubiquitin chains. With a focus on Ser65-phosphorylated ubiquitin, a key player in the intricate dance of mitochondrial quality control orchestrated by PINK1, the Phospho-TUBE will offer researchers an invaluable tool to efficiently isolate and analyze phospho-ubiquitinated proteins. This innovative addition to the TUBE family empowers scientists to delve into the nuanced dynamics of ubiquitin phosphorylation, providing a clearer understanding of its role in activating parkin and promoting mitophagy, particularly in the context of neurodegenerative conditions such as Parkinson’s disease.
Navigating the Ubiquitin Landscape: Applications of Phospho-TUBE
The applications of the Phospho-TUBE extend far beyond conventional ubiquitin research, offering a specialized lens into the realm of phosphorylated ubiquitin chains. As a stress-responsive signal induced by mitochondrial dysfunction, ubiquitin phosphorylation at Ser65 becomes a critical marker in the identification and study of damaged mitochondria. Researchers can leverage the Phospho-TUBE to unravel the complex interplay between phosphorylated ubiquitin, PINK1, parkin, and the autophagic machinery. With the ability to selectively bind and isolate phospho-ubiquitinated proteins, the Phospho-TUBE stands at the forefront of innovation, providing a gateway to uncover novel insights into cellular processes, particularly those implicated in neurodegenerative disorders. LifeSensors continues to drive progress in the field, empowering scientists with the tools they need to navigate the intricate ubiquitin landscape.
Charting a Course to Discovery
LifeSensors’ TUBEs stand at the forefront of ubiquitin research, offering unprecedented precision from Pan-Selective to Chain-Selective variants. These innovative tools not only enhance our comprehension of ubiquitin chain linkages and studying ubiquitinated proteins but also hold the key to transformative discoveries in cellular biology and disease mechanisms. As we step into the future, LifeSensors continues to empower researchers, illuminating the path to new insights and therapeutic interventions. With TUBEs, the journey of unlocking the secrets of cellular processes and studying targeted protein degradation is an ever-evolving narrative, guided by the promise of groundbreaking discoveries on the horizon.
References
- Mattern, M., Sutherland, J., Kadimisetty, K., Barrio, R. & Rodriguez, M. S. Using Ubiquitin Binders to Decipher the Ubiquitin Code. Trends Biochem Sci 44, 599–615 (2019).
