DUB Assays, Screening & Profiling
Advanced screening technology for quantitative measurement and drug discovery applications
Need Help?

- Understanding DUBs
Deubiquitylases (DUBs) are enzymes that can reverse the effect of E3 ligases by removing the ubiquitin from the target proteins. Unlike most E3 ligases, DUBs have inherent catalytic activity that is easily targeted by small molecules. These same DUBs are involved in ubiquitination maturation, recycling, and editing.
There are over 100 DUBs that can be divided into seven subfamilies, all capable of being encoded by the human genome. These DUBs have been implicated in many regulatory mechanisms, and biological functions, where they play a role in a plethora of clinical diseases.
Our DUB Platform Advantages
- High-throughput screening for modulators of DUB activity
- Patented assay platforms for characterizing DUB inhibitor compounds
- 35+ expressed and purified DUBs validated in HTS and compound profiling
- DUB-centric compound libraries for monitoring inhibition
- Di-, tri-, and tetra-ubiquitin chains of different linkages
- Platform Resources
LifeSensors DUBs Screening & Profiling Platform
Learn more about our comprehensive DUBs screening and profiling platform
- UbiProbe 384-well TR-FRET
Next Generation High-Throughput Screening
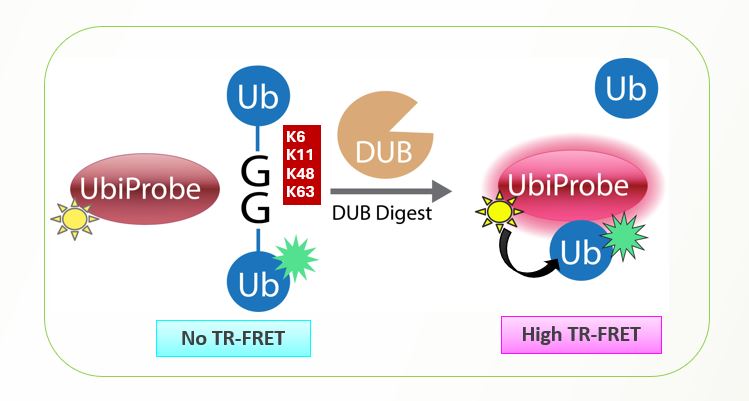
LifeSensors’ diubiquitin substrates represent a new class of substrates for the continuous fluorescent measurement of true isopeptidase activity. The IQF assay is expensive to run, requiring multiple different variations of IQF in order to properly screen for linkage-specific DUB activity.
The UbiProbe platform is designed to be a less-expensive, more complete platform for easier DUB screening avoiding the specific assay requirements of IQF screening, while also addressing manufacturing and background concerns sometimes associated with the IQF assay.
Service Highlights
Not only limited to linkage 48 or linkage 63 screening, the UbiProbe assay can also be used for K6, K11, K27, and K29 screening allowing a reliable assay for studying DUB cleavage in a consistent methodology.
Service Highlights
- Superior to Ub-AMC and CHOP Assays
- Greater Dynamic Range
- Amenable to high-throughput screening (HTS) and miniaturization
- Less compound interference
- Less Signal-to-background
- CHOP Assay
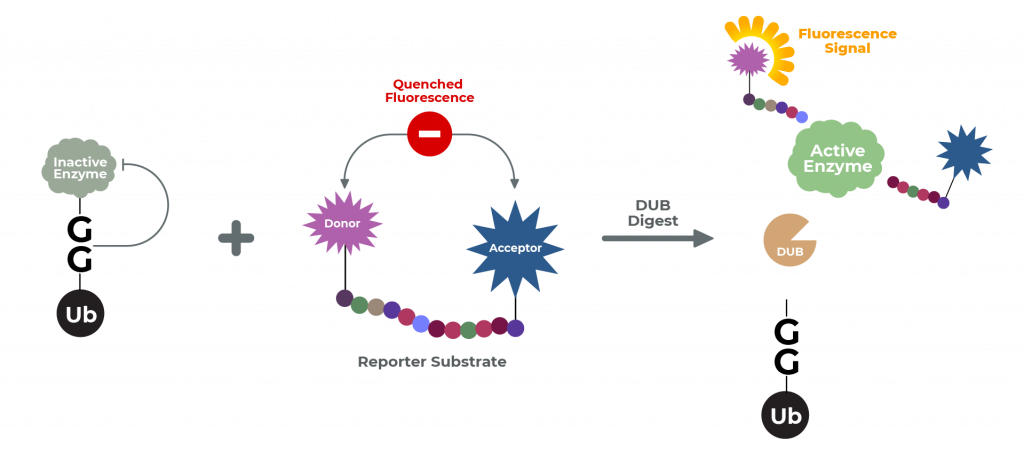
The Ub-CHOP2-Reporter Deubiquitination Assay consists of ubiquitin fused to a reporter enzyme, as well as a separate reagent substrate for the reporter enzyme. When fused to ubiquitin, the reporter is rendered catalytically inactive. Following cleavage of the Ub-reporter system by the isopeptidase, the free (and now active) reporter subsequently acts upon its substrate.
Thus, in this coupled assay, the signal generated by cleavage of the reporter enzyme’s substrate is a quantitative measure of isopeptidase activity. This assay utilizes the two classes of ubiquitin: ubiquitin-like proteins (UBL) and ubiquitin-domain proteins (UDP).
The UBLs function as modifiers in a manner analogous to that of ubiquitin. Examples consist of (and are available for this assay) SUMO, Nedd8 (aka Rub1), ISH15, Apg8, APg12, and Fat10. The ubiquitin-domain proteins consist of parkin, RAD23, and DSK2.
Service Highlights
- Superior to Ub-AMC and FRET-based assays
- Rapid and robust readout for DUB activity within 45 minutes with non-radioactive reporter substrates
- Amenable to high-throughput screening (HTS) and miniaturization
- Assay tests deconjugation of ubiquitin/UBL from a more physiologically relevant protein
- Unlike Ub-AMC, the CHOP2-Reporter system does not require excitation in the UV range (reducing the incidence of false-positives)
- Ubiquitin Fluorophore Assay
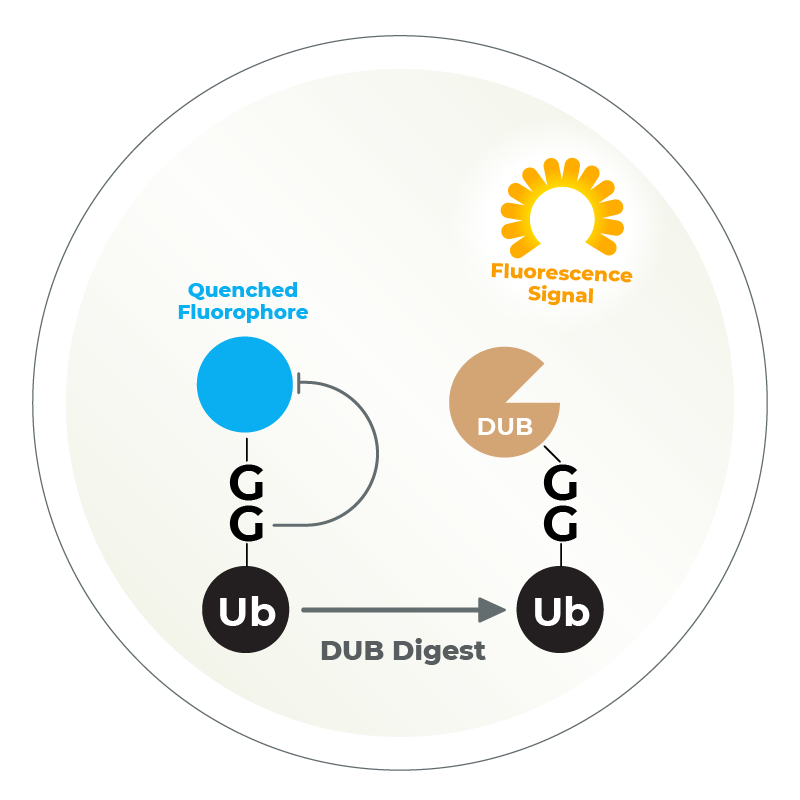
The Ubiquitin Fluorophore Assay utilizes a ubiquitin molecule bound to a quenched fluorophore (such as Ub-Rhodamine, Ub-AMC, or Ub-VME). After the DUB digestion takes place, the fluorophore is released and fluoresces, which is detected via a plate reader. This is the simplest and most straightforward high-throughput assay to measure DUB activity.
Ubiquitin Rhodamine (Ub-Rho) is a quenched, fluorescent substrate for DUBs, especially ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolases. Cleavage of the amide bond between the C-terminal glycine of ubiquitin and rhodamine results in an increase in rhodamine fluorescence at 535 nm (Exc. 485 nm).
LifeSensors has a multitude of various fluorescent substrates and DUBs to be used in these assays. These DUB assays utilize physiological substrates, polyubiquitin isopeptide chain-selective substrates, and several proteins attached to the C-terminus of ubiquitin that report a fluorogenic signal upon cleavage by DUBs.
Service Highlights
- High-throughput screening for modulators of DUB activity
- Determining activity and specificity of isopetidases for Ub/UBL-proteins
- In vitro detection of ubiquitin conjugation, determination of the activity of ubiquitin conjugating enzymes
- Substrate ID: DUBs
The Ubiquitin Proteasome System (UPS) controls the principal functions of almost all the cellular proteins of human cells and failures in this system often contribute directly or indirectly to the pathogenesis of many diseases, including cancer, inflammation, and neurodegeneration. There are ~100 deubiquitinases (DUBs) encoded in human genome and the functions of most of these DUBs remain unknown. Identification of substrates of individual DUBs is an essential step to unravel the cellular functions of DUBs.
Not only limited to DUBs, but there are also ~700 E3 ubiquitin ligases encoded in human genome and the functions of most of these E3s remain unknown. Recent development of PROTAC drugs to recruit E3 ligases and degrade therapeutic proteins highlight the value of studying E3 ligases. Substrate identification in individual E3 ligases is an essential step to unraveling cellular functions of E3s and identifying novel therapeutic targets. LifeSensors can help you identify the substrates of your preferred E3s and DUBs.
- Advantages of Choosing LifeSensors For Your Drug Discovery Project
In Vitro & In Cell Assays
Comprehensive assays to identify DUB & E3 substrates in controlled environments and cellular contexts
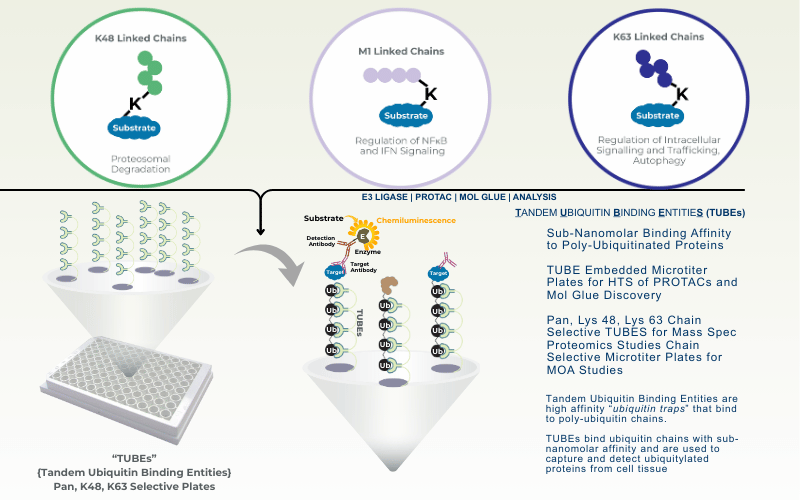
TUBEs for Detection
Advanced TUBE technology enables identification of direct deubiquitination targets
Substrate Trapping & Proteomics
State-of-the-art proteomic analysis to identify endogenous substrates with precision
Orthogonal Validation
Rigorous validation of substrates through independent orthogonal assay methods
- Diubiquitin IQF Assay (replaced by UbiProbe)
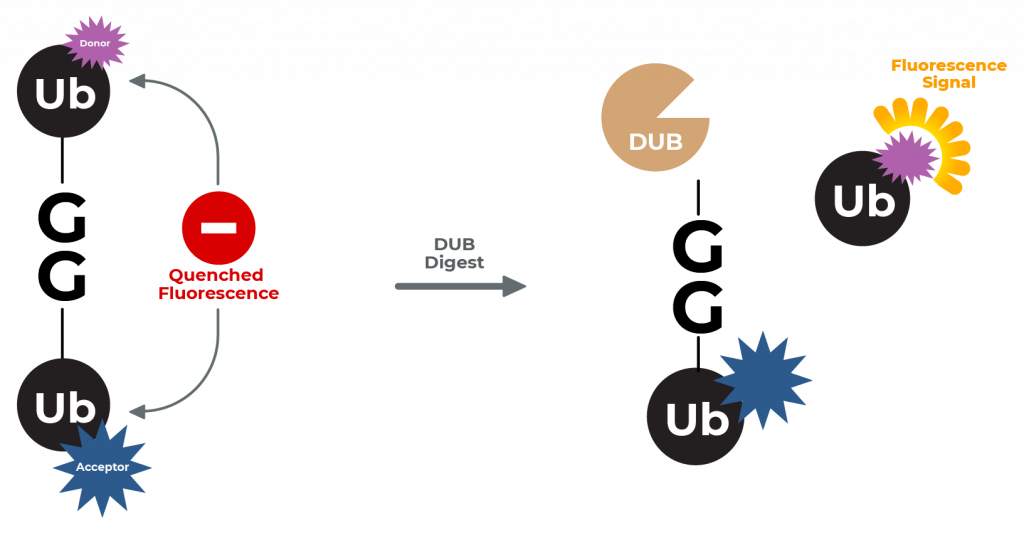
LifeSensors’ diubiquitin substrates represent a new class of substrates for the continuous fluorescent measurement of true isopeptidase activity. The IQF assay service utilizes a pair of conjugated ubiquitin proteins where one ubiquitin carries the fluorophore silenced by the nearby quencher present on the adjacent ubiquitin.
After DUB digestion, the quencher is cleaved from the Di-Ub and the fluorophore is now free to fluoresce and can be detected by a plate reader. This assay is physiologically relevant since the DUB cleaves a Ub-Ub bond! The assays are designed to study DUBs that interact with -K48, -K63 and -K6 linked diubiquitin.
C-terminus of wild type ubiquitin is conjugated via an isopeptide bond to lysine 48 (K48) of a second ubiquitin molecule with the resultant diubiquitin forming an internally quenched fluorescent FRET pair (IQF).
Service Highlights
There are multiple IQF Di-Ub variants that all have remarkable differences. In the case of K48- and K63- their 3D structure varies and can be used to measure various DUBs. For this reason, LifeSensors has created subpanels of IQF Di-Ub substrates with each linkage. Because each DUB is likely to recognize and cleave substrates with unique steric considerations, these subpanels vary in location of reporter fluorophore and quencher.
Our DUB screening assays include assay development where we empirically evaluate activity of DUB against the panel of IQF Di-Ub substrates to select the optimal fluorophore/quencher pairing.
Service Highlights
- Rapid and robust readout for DUB activity within 45 minutes with non-radioactive reporter substrates
- Amenable to high-throughput screening (HTS) and miniaturization
- Assay tests deconjugation of ubiquitin/UBL from a more physiologically relevant protein
- Unlike Ub-AMC, the CHOP2-Reporter system does not require excitation in the UV range (reducing the incidence of false-positives)
