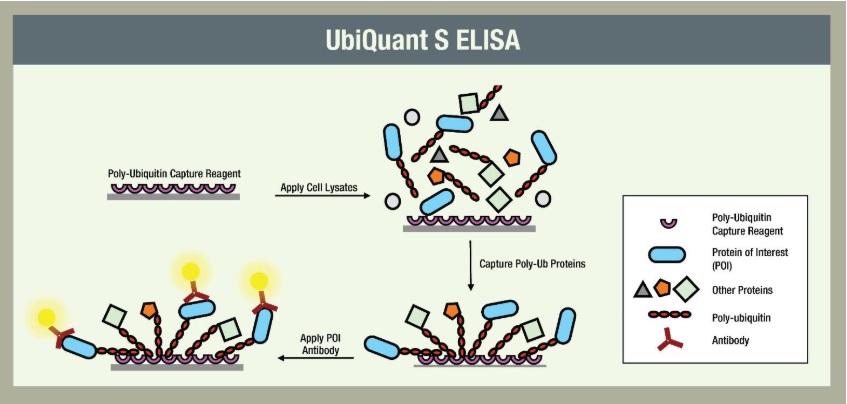
LifeSensors’ UbiQuant™ S ELISA and AlphaLISA assays are industry-leading platforms for measuring ubiquitylation of a target protein in cells. These assays utilize a proprietary polyubiquitin-binding entity to detect ubiquitylated substrates and are individually optimized for a specific substrate protein.
In the UbiQuant S ELISA assay, polyubiquitylated proteins are captured by an immobilized ubiquitin affinity matrix. Subsequently, unbound proteins are washed away, and ubiquitylated protein of interest bound to the matrix is identified using a POI-specific antibody and traditional ELISA detection reagents.
For low-abundant POIs, LifeSensors has developed a more robust form of the UbiQuant S assay called UbiQuant Ultra. This new generation of the UbiQuant family features plates coated with a high affinity polyubiquitin-binding matrix high, thus maximizing the chances that the ubiquitylated portion of the POI is captured.
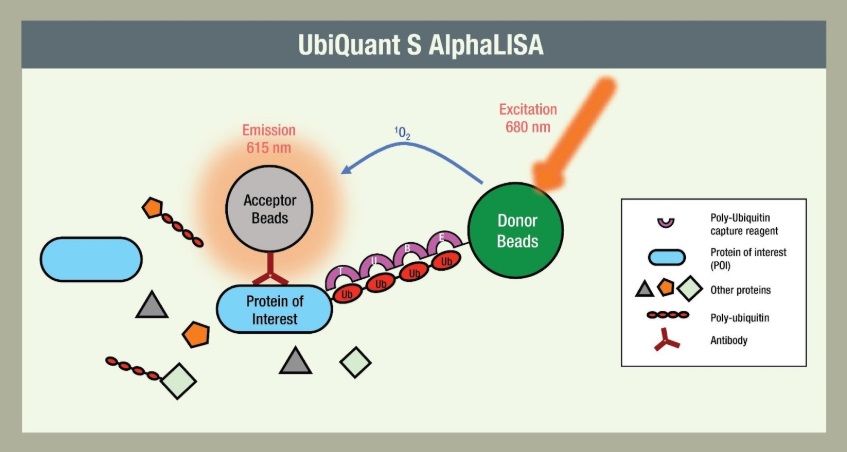
In the UbiQuantTM S AlphaLISA assay, TUBEs conjugated to AlphaLISA donor beads bind to polyubiquitylated proteins from a cell lysate. Simultaneously, POI antibodies conjugated to AlphaLISA acceptor beads bind to the POI in the cell lysate. If ubiquitylated POI is present, the concurrent binding of antibody and TUBE brings the AlphaLISA donor and acceptor beads into proximity, resulting in a luminescent signal that is quantitatively correlated to the level of ubiquitylated POI.
Advantages:
- UbiQuant ELISA allows for the testing of the effect of multiple compounds or conditions on the ubiquitylation levels of a POI in cell/tissue lysates.
- The UbiQuant S assays allow for the simultaneous monitoring the state of polyubiquitination as well as the protein levels of a POI.
- The UbiQuant S assays can be adapted to capture a portion of the POI with a specific polyubiquitin-linkage.
Applications:
- Confirmation of the potency and selectivity of the hits obtained from the in vitro assay.
- Monitoring the effect of PROTAC library on the polyubiquitination and protein levels of a POI in cell/tissue lysate.
- Monitoring the effect of multiple biological stimuli on the polyubiquitination and protein levels of a POI in cell/tissue lysate.
